 Introduction Introduction
Introduction Click to read Click to read
Internationalisation is the process of a company branching out to foreign markets to capture a greater market share.
The trend towards internationalization contributes to globalization - the state where economies worldwide become integrated due to cross-border trade and investments.
Internationalization may require companies to adapt their product features and branding to match the cultural and technological needs of the local market.
 |
|
 |
The attractiveness of a foreign market is assessed based on six factors:
1. The size and expected growth of the market
2. The accessibility of the market (geographical, political, legal, technological, social barriers)
3. The compatibility of different markets in the company’s portfolio
4. Resource availability and the distance to the target market
5. Competitive environment
6. External influences (PESTLE)
|
| As the world becomes more of a global village, internationalization has gained much discussion in recent years. What exactly is internationalization? How can an international company enter new markets? What are the advantages and disadvantages of international expansion? |
Objectives of Internationalization  Click to read Click to read
Goal Click to read Click to read
| Setting specific, measurable, actionable and time-bound goals for entering new markets around the world is a key to gaining a solid foothold in the global marketplace. |
 |
 |
Summing up Click to read Click to read
| Summing up |
 |
Business internationalization strategy
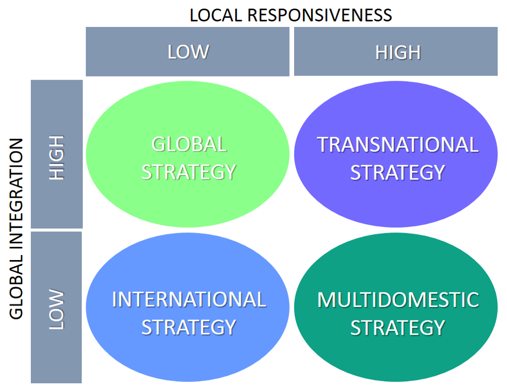
Companies with a multidomestic strategy have as aim to meet the needs and requirements of the local markets worldwide by customizing and tailoring their products and services extensively |
|
|
|
|
 |
Goal
Setting specific, measurable, actionable and time-bound goals for entering new markets around the world is a key to gaining a solid foothold in the global marketplace. |
 Be open to possibilities Be open to possibilities
Achieve growth Click to read Click to read
| The local market may have a limited customer base or become saturated over time, expanding overseas is the only for businesses to increase their market share and continue growing. |
 |
Improve profitability Click to read Click to read
| International businesses can take advantage of marketing and technological advantages in the host country or introduce higher prices to new customers to achieve higher profits. |
 |
Increase competitiveness Click to read Click to read
| Companies operating overseas have greater economies of scale to lower the cost of their business and be more competitive. The presence on a global scale also boosts the company’s reputation and allows it to attract more customers compared to local businesses. |
 |
Summing up Click to read Click to read
| Summing up |
 |
Achieve growth
Expansion abroad is the only option for companies to increase their market share and continue their growth. |
|
 |
Improve profitability
Exploiting market and technological advantages to achieve profit |
|
 |
Increase competitiveness
A global presence also strengthens the company's reputation |
 Managing the Entering to new markets Managing the Entering to new markets
Export Click to read Click to read
| |
One major challenge of an international business is to manage change in an effective and coherent manner. |
 |
| |
| Set up a direct investment. The company setups manufacturing overseas or takes over or merges with a foreign business. Although direct investment allows the business to cut down on tax and transportation costs, it’s also the highest risk and most expensive option out of four market entry modes. |
Licening/Francising Click to read Click to read
| The original business licenses other firms to manufacture and sell its products. The licensee pays a fee to reserve a trademark of the licensor’s products. Franchising is the same as licensing, only that the original business still has some control over the manufacturing and marketing processes of the licensees. This approach is much more economical than setting up a foreign facility or taking over the local business. |
 |
Joint ventures  Click to read Click to read
| Establish joint ventures. The company partners with an overseas business take advantage of its know-how upon entering a new market. |
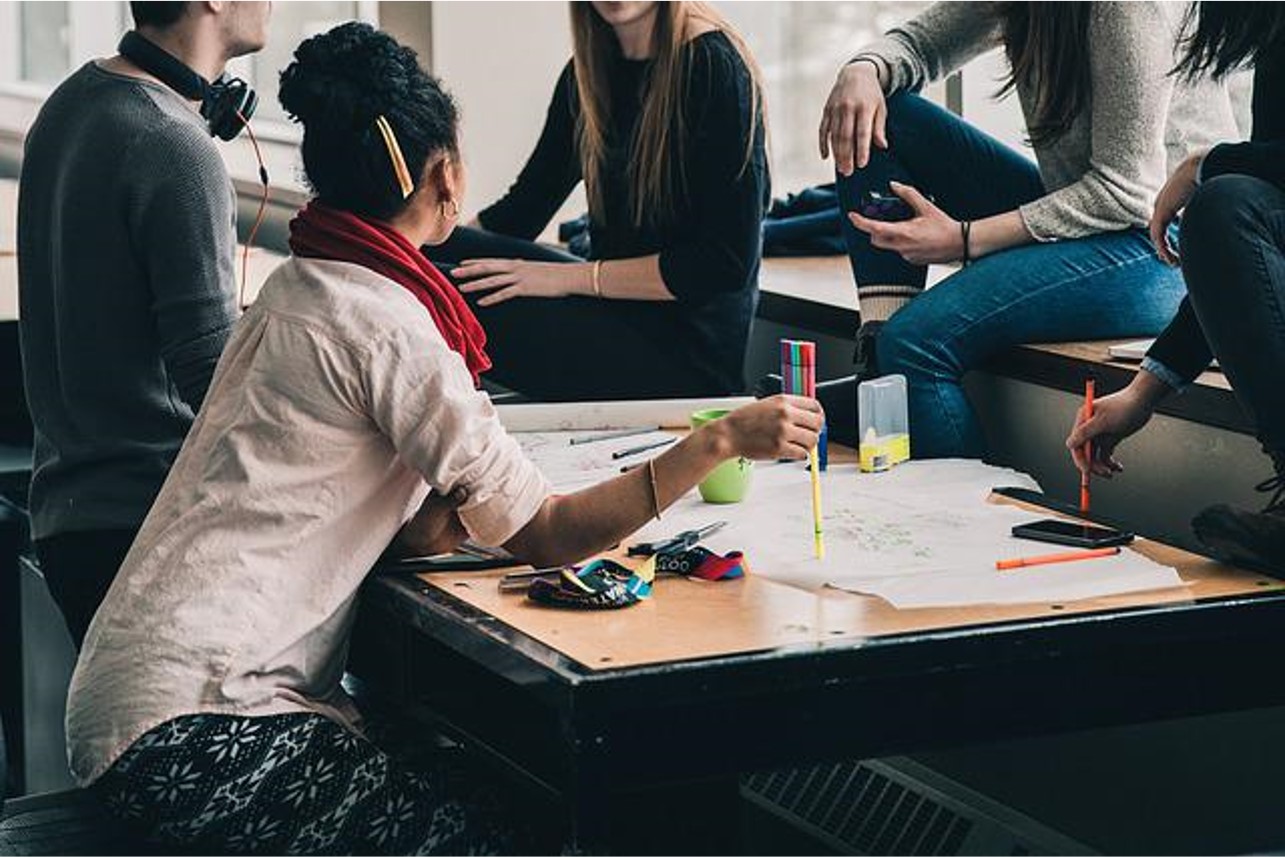 |
| |
|
 |
Summing up Click to read Click to read
| Summing up |
 |
Set up a direct investment
The company setups manufacturing overseas or takes over or merges with a foreign business. |
|
 |
Discover Licensing
The original business licenses other firms to manufacture and sell its products. |
|
 |
Establish joint ventures
Taking advantage of other companies know-how. |
 Plan Preparation Guidelines Plan Preparation Guidelines
Clearly define the objectives for producing the plan  Click to read Click to read
| |
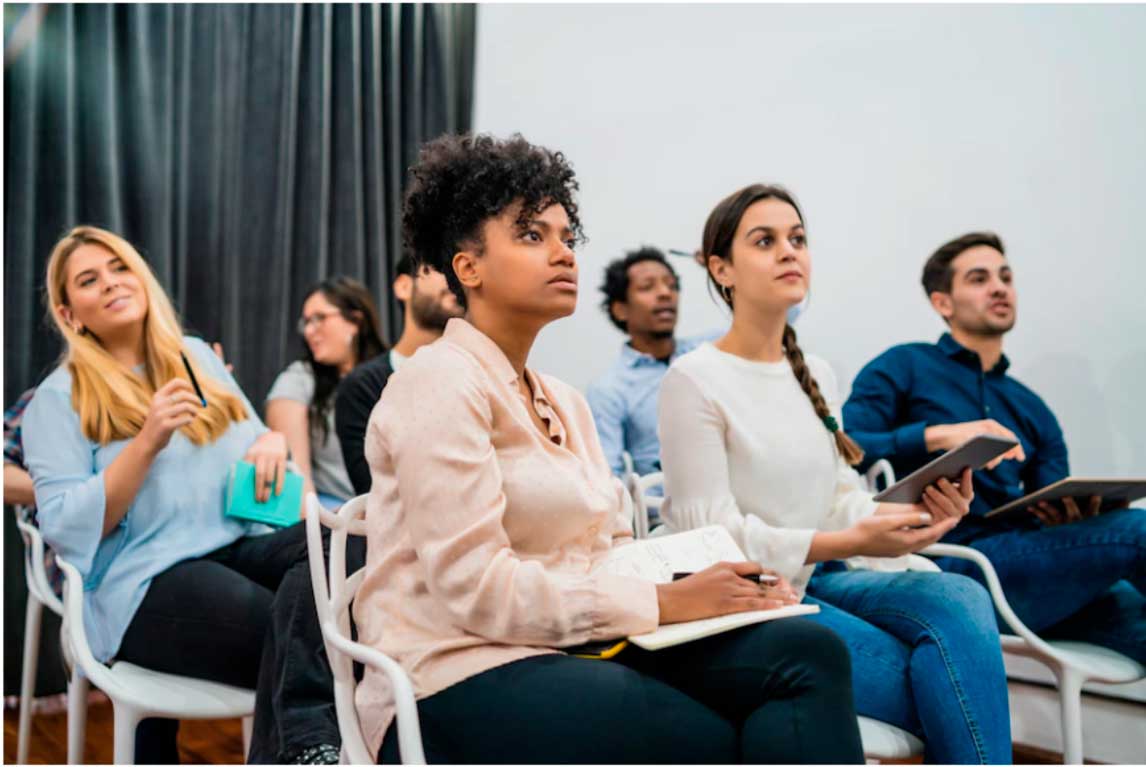 |
| Who is going to read the plan, and what will they need to do? These objectives can help you decide how much emphasis to put on various sections. |
| |
| The international business plan is the culmination of all of the work done to determine the appropriate venture for the organization’s growth. As part of the feasibility process, the organization will have determined its own internal readiness, conducted comprehensive target market research and carefully analyzed any relevant risks |
Allocate sufficient time and resources to thoroughly research the plan Click to read Click to read
| |
|
Guidelines that help managers to make better decisions. |
| A plan is only as good as the research that went into producing it. |
 |
| |
|
Ensure financial projections are believable Click to read Click to read
| For many readers, the financial section is the most important part of the plan because it identifies the financing needs and shows the profit potential of the business. In addition, a good financial plan will give the reader confidence that the author really understands the business. |
 |
Summing up Click to read Click to read
| Summing up |
 |
Define the objectives for producing the plan
To decide how much emphasis to put on various sections. |
|
 |
Allocate sufficient time and resources
A plan is only as good as the research that went into producing it. |
|
 |
Ensure financial projections are believable
A good financial plan will give the reader confidence that the author really understands the business. |
 Impact on different functions of business Impact on different functions of business
Human resources  Click to read Click to read
|
Internationalization processes can lead to changes in the Human and Resources department of the company.
- Managers may need to go under training or get advice from advisors to hire an international workforce.
- Multinational companies may also face cultural and legal problems when hiring and motivating foreign workers.
- Offshoring may trigger resentment among underpaid workers in developing countries.
- Licensing and franchising may require the company to develop thorough training programs to maintain the quality and culture of the original business.
|
|
| Internationalization can affect various business functions, including human resources, finance, marketing, operations, and management. |
| |
Marketing Click to read Click to read
|
A lot of marketing decisions are associated with the internationalization process.
- Extensive market research has to be carried out to ensure the product is needed abroad Some customers may prefer a product made in a certain country than the other, e.g. Made in the UK.
- Introducing new products to a foreign market also uses up a considerable amount of market. There are also marketing costs to competing with businesses in the host country.
|
 |
Finance Click to read Click to read
|
The expansion to other territories requires a substantial investment which incurs many risks for the international business.
- Setting up a manufacturing facility broad or acquiring a foreign business can take up a lot of financial resources. However, there’s no guarantee this will generate a positive return.
- Offshoring can reduce costs of production but there might be hidden costs when the company switched back to producing locally.
- Franchising, licensing, and exporting are much less risky ways in terms of finance for a global business.
|
 |
Summing up Click to read Click to read
| Summing up |
 |
Human resources
Internationalization processes can lead to changes in the Human and Resources department of the company. |
|
 |
Marketing
A lot of marketing decisions are associated with the internationalization process. |
|
 |
Finance
The expansion to other territories requires a substantial investment |
 Communication Communication
The importance of intercultural communication Click to read Click to read
| In business, intercultural communication allows individuals to interact respectfully and constructively. It encourages the finding of common ground and an honoring of differences. |
|
Intercultural communication is equally important in person, on the phone, and even via email or text message. It can help with things like:
- Creating a hiring process that prioritizes hiring diverse candidates
- Fostering existing client relationships
- Improving internal communication within a diverse, intercultural team.
|
 |
Overcome the Barriers  Click to read Click to read
| While intercultural communication is important, it doesn’t always come easy. Numerous communication barriers can threaten the integrity of an organization, such as: |
- Assuming similarities: assume cultural similarities between individuals,
- Language barriers: The inability to overcome language barriers can be one of the most intimidating communication barriers of them all.
- Ethnocentrism: The tendency to assume the superiority of one’s own culture can often hamper intercultural communications.
|
 |
Improve your intercultural business  Click to read Click to read
|
Educate yourself
Educating yourself through communication can help you round out your view of different cultures and approach each interaction with an open mindset.
|
|
Learn a language
Simply making an effort to learn another individual’s language — no matter how successful that effort may be — shows that you care and are invested in meeting the other person on their terms.
|
|
Be aware of nonverbal communication
Numerous nonverbal factors can help inform the conversation. Things like posture, eye contact, and tone of voice can all be critical.
|
Summing up Click to read Click to read
| Summing up |
 |
The importance of intercultural communication
Intercultural communication allows individuals to interact respectfully and constructively. |
|
 |
Barriers
Numerous communication barriers can threaten the integrity of an organization. |
|
 |
Improve your intercultural business
- Educate yourself
- Learn a language
- Be aware of nonverbal communication
|
|
 Business plan for internationalization
Business plan for internationalization
 Introduction
Introduction Click to read
Click to read  Click to read
Click to read  Click to read
Click to read  Click to read
Click to read  Be open to possibilities
Be open to possibilities  Click to read
Click to read  Click to read
Click to read  Click to read
Click to read  Click to read
Click to read  Managing the Entering to new markets
Managing the Entering to new markets Click to read
Click to read  Click to read
Click to read  Click to read
Click to read  Click to read
Click to read  Plan Preparation Guidelines
Plan Preparation Guidelines Click to read
Click to read  Click to read
Click to read  Click to read
Click to read  Click to read
Click to read  Impact on different functions of business
Impact on different functions of business Click to read
Click to read  Click to read
Click to read  Click to read
Click to read  Click to read
Click to read  Communication
Communication Click to read
Click to read  Click to read
Click to read  Click to read
Click to read  Click to read
Click to read 





















